MDA against Lymphatic Filariasis in Odisha
Odisha’s microfilarial rate at the beginning of the ELF program in 2004 was 2.6, and had dropped to 0.68 in 2015
Progress in the elimination of LF

NVBDCP
CONTENTS
KEY INSIGHTS
Odisha’s experience offers relevant lessons to inform decision making across other states to enable cost, time, and effort savings.
States that are currently implementing MDA and facing challenges with lack of awareness can draw lessons from Odisha’s rigorous information, education, and communications activities and multichannel social mobilization strategies. In case of resource constraints, states can leverage Odisha’s partnership approach to bring in community-based organizations to reduce time, cost, and effort. Lastly, states that are focused on improving the knowledge and skill of their staff members can use the learnings from Odisha’s targeted training and capacity-strengthening efforts to customize and improve training outcomes.
ADHERENCE TO NATIONAL GUIDELINES WITH LOCAL ADAPTATIONS
Odisha’s strict adherence to the national guidelines, along with adaptations to the local context, enabled smooth implementation of MDA

Odisha communicated the guidelines effectively across all levels of implementation, which ensured understanding of the guidelines and greater compliance. The guidelines streamlined actions at all levels, and contextual references and translations of guidelines enabled easy reference to ground realities during training.
Collaboration Across Departments
Multi-stakeholder coordination committees set up by the state were responsible for charting the course of MDA implementation and therefore played an important role in enabling collaboration across departments for planning purposes
At the state and district levels, the state task force, state technical advisory committees, and district coordination committees were set up and held regular meetings. These committees provided stakeholders with the platform to identify and anticipate challenges in the MDA campaign, and consequently come up with strategic solutions to mitigate them.

Effective Leadership and Human Resource Management
Stakeholders, operational officers, and leaders at all levels displayed a high degree of motivation and ownership for the MDA program, going above and beyond their predefined duties to ensure success

The committed leadership were able to avoid disruptions and guarantee smooth MDA implementation by accounting for particularities of their local context, creatively mobilizing staff, and ensuring rigorous training across levels.
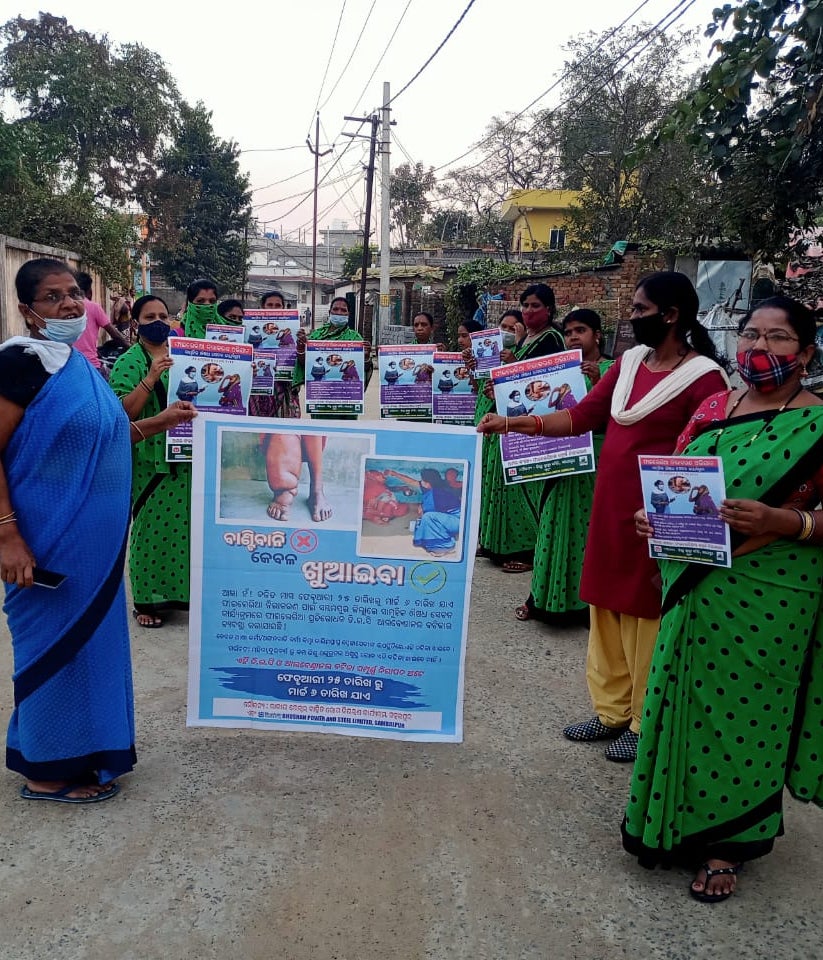
Engagement with Local Influencers and Social Mobilization Campaigns
Odisha’s experience in engaging and mobilizing the community demonstrates the value of robust communication and social mobilization strategies
Odisha customized its communication efforts to the local context to facilitate absorption of the information by all communities. Odisha health officials also leveraged local influencers to generate momentum for the MDA campaign. Communication efforts were intensified closer to MDA rounds to ensure that no one remained unaware of the program.

Adaptation of Learnings from Previous Public Health Interventions
Lessons, assets, and resources from previous programs accelerated MDA planning and provided the experience needed to anticipate and mitigate implementation challenges in Odisha
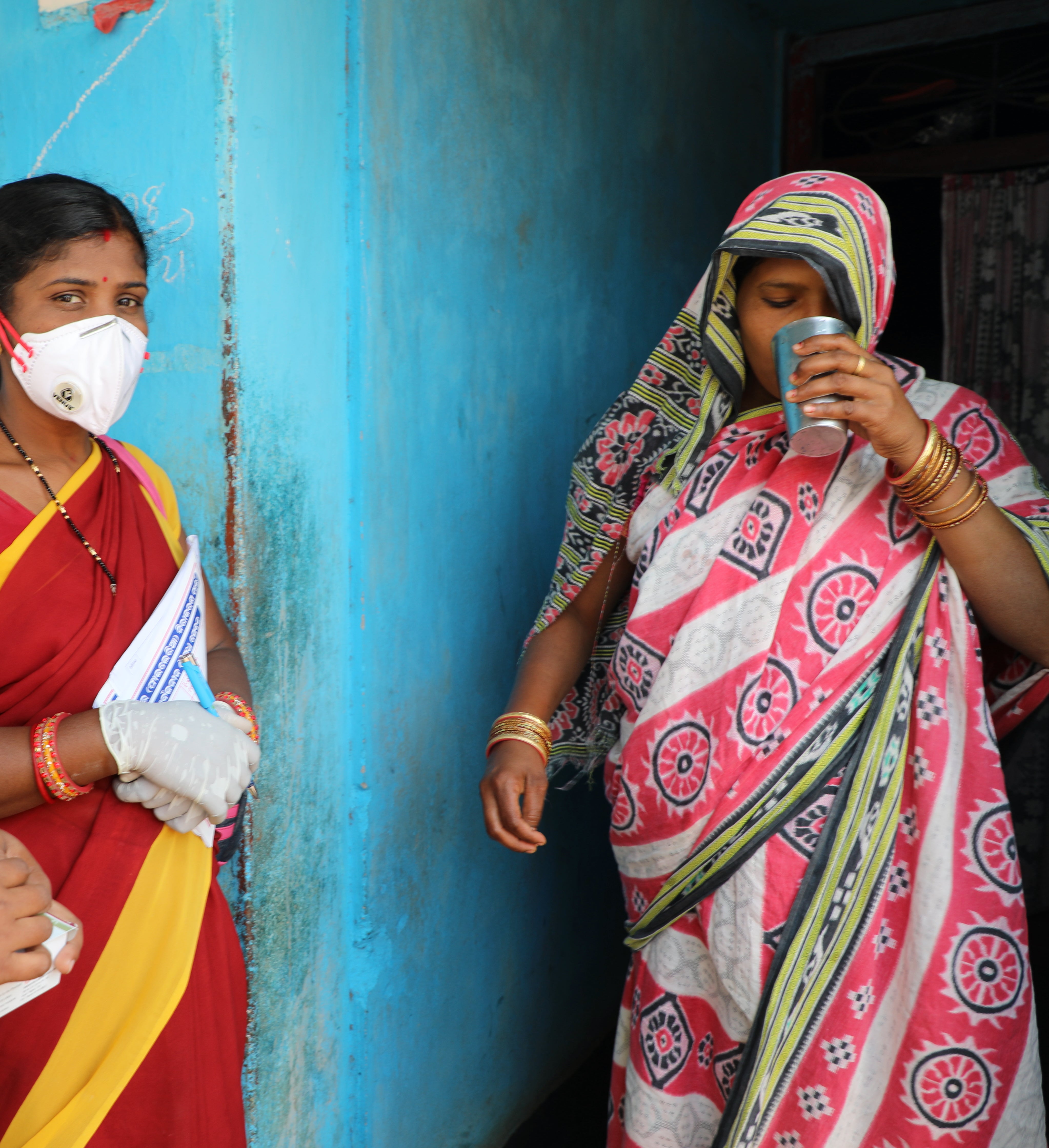

Experienced staff from other public health programs were closely involved in the planning, implementation, and monitoring of the ELF, bringing a wealth of experience to increase the effectiveness of the MDA program. This allowed the implementation team to anticipate and mitigate challenges in MDA implementation based on their experience with other health programs.
MDA against Lymphatic Filariasis in Odisha

Ask an Expert
Our team and partners are available to answer questions that clarify our research, insights, methodology, and conclusions.
